How can Social Media be Socially and Inclusive in Healthcare in the New Normal?
With the recent US Government action on Facebook and the pace at which fakenews have been spread during Covid and now on the Covid Vaccine, I am tempted to share my earlier article on this subject.
Background
India is world’s second largest growing online population in the world after Brazil. Over the last one year, India witnessed a YoY growth of 31% in people going on the internet, making it the world’s third largest population on the internet. More importantly, this growth has been fuelled people using tablets and smart mobile to go online. However when we look at in absolute terms, only 73.9 million people were on the internet (less than 10% of India’s mobile connected population) of this only 86% of the population (63.55 million) is using social media. While the use of healthcare online grew by 17% last year, it is still lower than retail sector’s growth of around 80% last year. It is fairly evident that several vertical online and social media options have sprung up in India, which has led to the heady growth in retail social media in India. Social media is not about page views, eyeballs or clicks (see box – What is Social Media?). Healthcare is no exception to this, as social media platforms radically changes the nature of business relationships. While over $ 750 million was invested in social and online retail business models last year, why has online and social healthcare business models and solutions remained a laggard in India?
| What is Social Media? |
| Social Media is different from other communication platforms and channels in four ways: |
| Content is generated and governed to a varying degree by the users |
| Communities connect people with common life experiences, preferences and interests |
| Information can be developed quickly and distributed broadly |
| Open, interactive dialogue and information sharing among media users is encouraged |
| Top – 10 Need-to-Knows about Social Networking and Where It’s Headed |
| Social networking is the most popular online activity worldwide Social networking behavior both transcends and reflects regional differences around the world The importance of Facebook cannot be overstated Short Content and Microblogging has emerged as a disruptive new force in social networking Local social networks are making inroads globally It’s not just young people using social networking anymore – it’s everyone “Digital natives” suggest communications are going social Social networking leads in online display advertising, but lags in share of dollars The next disrupters have yet to be decided Mobile devices are fueling the social addiction |
The Social Media Landscape
Today there are over 450 social networking sites globally and they collectively serve over 6.5 billion registered users. Nearly 1 in 5 minutes online is spend online on social media, with Facebook getting a lion’s share of the time spent on social media. Healthcare consumers are now starting to leverage social media globally and in India. However, healthcare decisions or dis-engagement at any point in time with the decision making process is a very complicated process and there are many factors associated with this in the social media usage. Nor this is about hospitals putting up their Facebook pages, doctors in India putting up their profiles on Linkedin or some surgeon’s putting up their videos of their procedures on You Tube. This fragmentation has led to assessing not only beyond Facebook, Linkedin, Google+, Twitter, Instagram and You Tube.
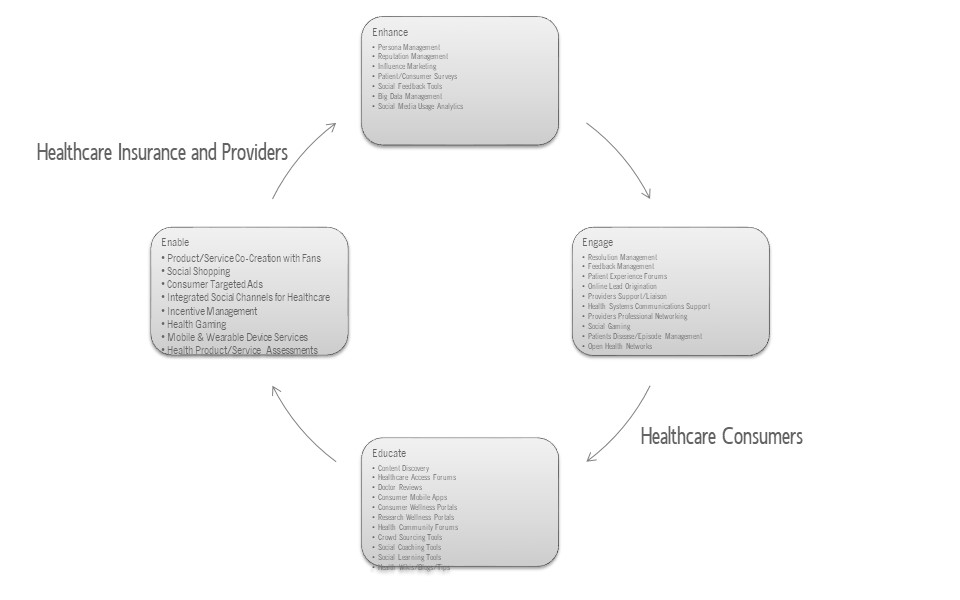
Understanding the 4Es in Social Media Usage in Healthcare
Enhance
These are players who enhance and push content into the social community. By seeding conversations and then enhancing it, healthcare companies create and perpetuate an ongoing focus group that can help identify opportunities to create, enhance and modify products and services for consumers. These also include tools that enable the social media networking
Engage
The are platform that are used by healthcare providers, payers and employers to communicate and create a dynamic interaction with their community of patients, members and professional affiliates
Educate
There are several platforms where user generated content and shared learning supports improved healthcare.
Enable
Enabling consumers to take a lead role in finding, sorting and acting on health information.
There are over 40 different micro-segments from the 4Es for social media features and services that can be offered by different social media platforms in healthcare. This is where there is opportunity for Indian social media platforms in healthcare to emerge and grow out globally. Analyzing the marketplace for vendors marketing social tools related to healthcare and I found a wide variety of business models and
strategic approaches. Of the numerous healthcare-centric solutions, many are geared toward consumer use, most are small and a scant few have “platform features” where broad social initiatives could be supported.
| 4Es of Social Media in Healthcare | Representative Companies in India and Globally |
| Enhance | LiquidGrids, Listenlogic, Pharmawall, Semantelli, Welltok, NodeXL, Gephi |
| Engage | Shapeup, ExtendMD, FairCareMD, HealthCrowd, QuantiaMD, RN Rounds, Sermo, Wellness Layers, Healthcaremagic, |
| Educate | There are about 150 players here in India and abroad |
| Enable | Snapdeal, Groupon, CarePages, eCareDiary, FitBit, Digifit, Endomondo, Gamercize, HealthCentral, LivingSocial, ZocDoc, 15 sites in India |
Roadmap to Business Models for a Social and Inclusive Social Media in Healthcare in India
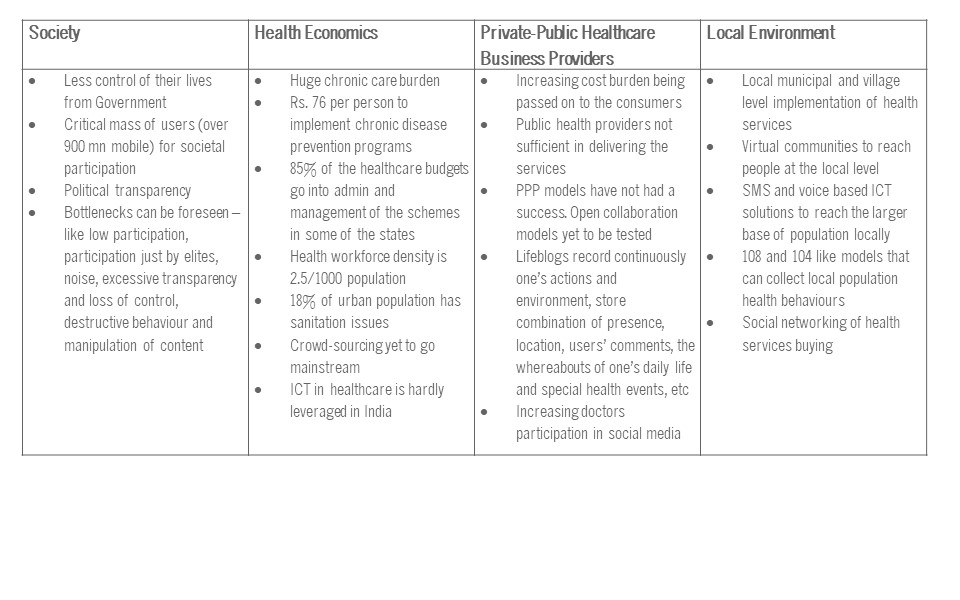
As you will notice from the table above, there are handful of social media business models or platforms in healthcare that have emerged out of India even though there is a huge potential to tap the huge mobile teledensity of close to 900 million. We have tapped less than 10% of this, even though healthcare is an important part of the way people live, work and communicate in India. How do we create a similar platform for rural areas, where Internet platforms are not usable due to literacy, access, and affordability challenges? Building on from my work at the Health and ICT Minister’s Panel for Africa in the last decade. The key takeaways from my work in the emerging market with respect to healthcare, ICT and social media is that these business models will be successful only when:
Transparency
The transparency of activities is a key feature in social media; health is a subject affects private provider companies, public administration as well as consumers
Rise of ubiquitous participatory communication model.
Newspapers, urban spaces and television will all be supplemented with interactive social media applications.
Reflexive empowerment.
Healthcare empowerment through social media is mostly reflexive, i.e. it is usually based on a specific issue and temporary coalitions that engage in dialogue on the topical issue.
Personalization/fragmentation versus mass effects/integration.
Practices and services in the web can be tailored and personalized to almost every detail with the help of portable profiles. Simultaneously, social media opens vast potential also for enormous mass effects and integration.
New relations between physical and virtual worlds
Practices induced by social media, e.g. communication, participation, co-creation, feedback and rating, get more common in daily environments and in urban spaces.
Key Drivers to Social Networking
There are 12 key drivers that need to be broadly analysed for developing social networking business models in (see box) in healthcare in India and that can then be exported to other emerging markets. Every business model in social networking in healthcare would pick 2-3 key drivers to disrupt the social networking landscape as described earlier.

Creating a Framework for Transformative Business Models in Social Media in Healthcare
Countries like Finland, Singapore are experimenting these models of social media networking for healthcare. There are several analytical tools being used to analyse this networking effect. One such tool is illustrated in the box below:
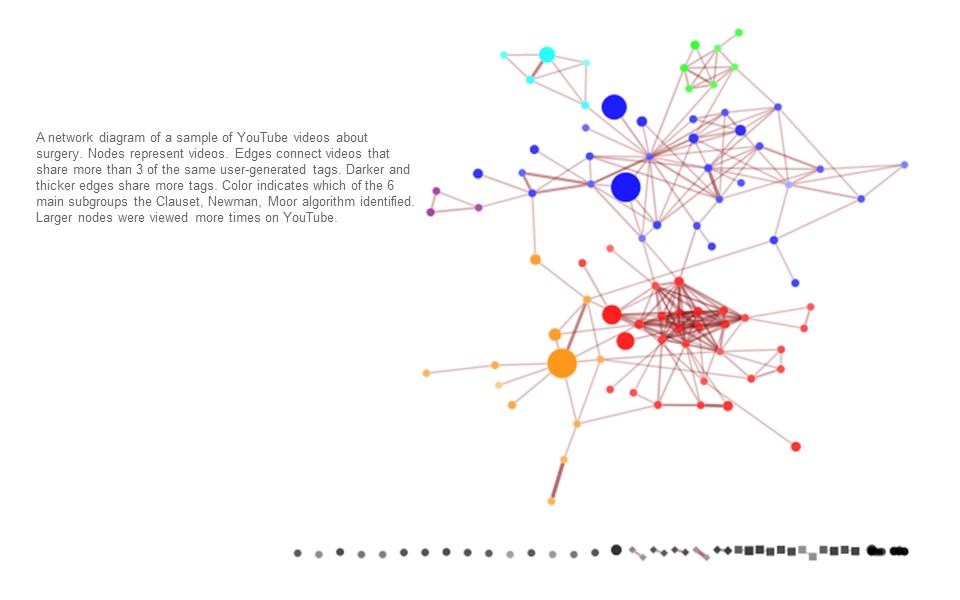
Charting out and exploring the social network relationships
As we are increasingly surrounded by a by a sea of tweets, e-mails, blogs, wiki pages, videos, wall posts and different apps that enable the social networking. It is important for any new business model to map out these relationships to understand where the gaps are in the overall social network landscape (4Es given earlier).
Not all social media networks include people as nodes. Some include content of interest, such as videos, images, or wiki pages. Increasingly, data from social media sites such as tags, comments, purchasing patterns, and ratings can be used to link related content together into networks. Viewing content as a network can help learners make sense of how individual concepts or experiences fit into a larger whole. They can provide a view that provides perspective on an entire field of knowledge so that information that is most relevant can be identified. The goal is to provide an overview on surgery, many of which can be used to help educate medical students, professionals, and consumers. It may be useful in finding relevant content and its relationship. Companies or educational institutions interested in medical content may use such a map to inform their decisions about what videos to post and how to carve out a unique niche in the existing information landscape. Or they may decide that their solution has a poor selection of videos on the topic of interest
Social Network Map of Surgery on You Tube
Case Study: Gram Vaani: Taking Social Media to the Masses
Gram Vaani is voice based social media network accessible from ANY phone (not a smart phone connected to a EDGE or 3G network). They have developed the novel concept of voice based social media, wherein they enable people to express themselves and share information in voice through ordinary phone calls. People can call into our toll-free number and leave messages or listen to messages left by other people (post moderation). It has captive user base of 35,000 families, over 2,000 impressions made per day. This enables
- bottom-up information sharing where people ask questions and others from the same community help answer these questions, or share stories and experiences, and
- accountability by giving reports on the performance of government schemes, demanding better performance from local and state social welfare providers, and policy inputs.
Their network in Jharkhand has seen several cases where reports filed by people led to redressal action by the government departments including healthcare, and the platform is also used regularly for information seeking on agriculture, livelihoods, health and education, and even cultural expression through folk songs and poetry. They have ability to run sponsored channels and programs and to incentivize local entrepreneur networks to conduct social marketing. 90% community sourced content which includes local news, interviews and informational services, opinion on topical issues, guided discussions and campaigns, grievances and feedback on government schemes, cultural artifacts including folk songs and poems. 98% of the users of this social media platform is educated class 12 and below. This platform is also very interesting for a vertical health through rural social media application.

Summing Up
India is a typical to many other emerging markets where social media has only penetrated the urban and the educated sections of the society, while over a large majority 90% of the mobile population is still not seen the face of the Facebook. Healthcare is now emerging as investments in retail sector have penetrated deeper into India. We need business models that can become the next twitter or facebook in India. Folks like Graam Vaani have demonstrated in a small way that they can bring social media to the mobile connected populations of India and emerging markets. It is time to look at the 4Es of healthcare social media and start building vertical healthcare solutions on top Creating a Socially and Inclusive Social Media in Healthcare in India