Preamble
Various Industry Bodies are working with Niti Aayog for the Viksit Bharat@2047 policy recommendations. Mine was on the Amrit Kaal for healthcare for all by 2047. Parts of the thinking has been outlined in some our my blogs and podcasts. Read Amrit Kaal : Budget 2022 | Kapil Khandelwal KK.
But an interesting announcement by Russia came across my eyes and it makes me wonder on the timing and its effectiveness. Recently, Russia announced a new Ministry – The Ministry of Sex. The title of the Ministry may sound obscene, but its objectives are not to regulate illicit sex in the country. I can understand that is part of a broader effort by Russian authorities to reverse the country’s demographic decline, due to the fatalities suffered by the Russian in the ongoing conflict with Ukraine. In 2024, Russia’s birth rate is approximately 11.108 births per 1,000. This represents a slight decline from the previous year.
Let’s understand the objectives of this new Ministry in Russia and similar initiatives around the world and in India to improve their demographic dividends.
What is Ministry of Sex?
Russia’s Russia aimed at addressing the country’s declining birth rate. The idea is to create a dedicated government body to coordinate various efforts to boost the population and birth rate to derive demographic dividends in the future. Some of the proposed measures include:
- Turning off the internet and lights between 10 PM and 2 AM to encourage intimacy among couples;
- Financial incentives for first dates, with the government paying up to 5,000 roubles (around ₹4,395);
- State-funded wedding nights in hotels, with expenses covered up to 26,300 roubles (around ₹23,122); and
- Compensation for stay-at-home mothers for household chores, which would count towards their pensions.
Let us understand if such measures can lead to increase in babies in Russia.
Key Drivers of Increasing Birth Rate of a Country
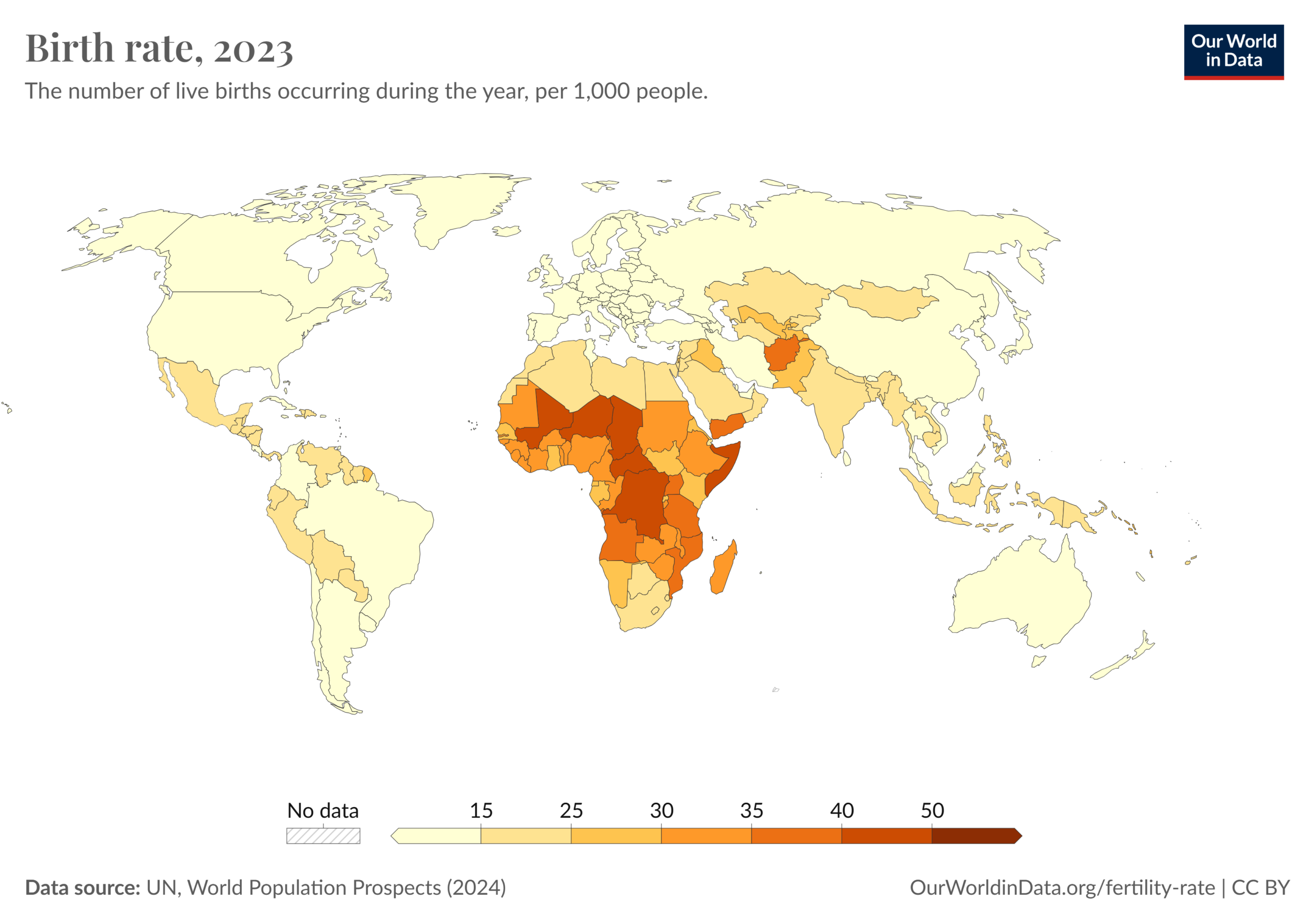
Russia is not alone as a country that is witnessing the decline in the population due to birth rate. See Map.
While Russia’s measures to regulate couples to encourage more sex and babies in the short-term is laudable, the key drivers to improve the birth rate of a country are dependent on multiple factors addressing various social, economic, and policy-related factors. Here are some key drivers:
- Economic Stability and Growth: Economic prosperity can encourage higher birth rates as families feel more secure in their financial future.
- Affordable Childcare and Education: Providing affordable and high-quality childcare and education can reduce the financial burden on families and make it easier for parents to balance work and family life2.
- Parental Leave Policies: Generous parental leave policies, including paid maternity and paternity leave, can support parents during the early stages of child-rearing.
- Housing Policies: Affordable housing can make it easier for young families to establish a stable home environment, which is conducive to having more children.
- Healthcare Access: Ensuring access to comprehensive healthcare, including reproductive health services, can help families plan and support larger families.
- Work-Life Balance: Policies that promote flexible working hours and remote work options can help parents manage their professional and personal responsibilities more effectively.
- Social and Cultural Support: Creating a family-friendly culture that values and supports parenthood can encourage higher birth rates. This includes community support systems and positive societal attitudes towards families.
- Financial Incentives: Direct financial incentives, such as child allowances, tax breaks, and subsidies for families with children, can alleviate some of the economic pressures associated with raising children.
- Education and Awareness: Promoting awareness about the benefits of family planning and providing education on reproductive health can empower individuals to make informed decisions about having children.
- Social Media Blackouts: This is a new one coming from Russia. Reducing social media chatter and addiction can improve sexual health and sex.
Addressing these factors comprehensively can create an environment that supports and encourages higher birth rates in a country. Let’s compare these with some of the measures taken by some of the countries to increase their birth rates in their country.
Birth Rate Increasing Measures by Country
Here are some examples of countries that have taken measures to increase the birth rate in their country by encouraging couples to have more babies.
| Country | Measures | Other Unique Measures |
| Singapore | · Financial incentives
· Housing benefits · Extended parental leave |
· Promote dating events and matchmaking services to help singles find partners |
| Japan | · Subsidized childcare
· Parental leave · Financial incentives |
· Community programs to encourage social interaction and dating among young people |
| France | · Generous family policies
· Extensive parental leave · Subsidized childcare · Financial incentives |
· France has the most generous family policies in the EU to promote family welfare
· Free education and healthcare for children |
| South Korea | · Financial incentives
· Community programs for parental support |
· Financial support for fertility treatments
· Policies to improve work-life balance and family and family-friendly workplaces |
| Hungary | · Financial incentives
· Tax benefits |
· Loan waivers for having multiple children
· Subsidies for housing and car purchases |
| Greece | · Tax benefits
· |
· Subsidies for childcare
· Payments for new parents |
| Poland | · Financial incentives | · Known for its “Family 500+” program,
· Monthly payments to families for each child |
Anti-Measures That Accelerate Ministry of Sex Type Initiatives Around the World
There are several anti-measures or counter trends that are accelerating the Ministry of Sex type of initiative around the world in the future to provide incentives people to marry, starting a family. Some of them, though not an exhaustive list are as under:
The #MeToo Awakening:
The #MeToo movement has contributed to a broader cultural shift that affects how people view and approach relationships, which in turn may be impact birth rates, although it is early to establish a co-relation. In the U.S., there was a notable drop in the number of babies born in 2017, with an estimated 3.84 million births, down by more than 100,000 from the previous year. This decline has been partially attributed to the “romantic reckoning” following the #MeToo movement. The societal changes after the #MeToo has many counter trends. These include:
- Increased Awareness and Caution: The movement has heightened awareness about consent and respectful relationships. This has led to more cautious and deliberate romantic interactions, which has delayed relationship progression and family planning of the past.
- Shift in Social Dynamics: The emphasis on addressing and preventing sexual harassment has changed how people approach dating and relationships. This shift can lead to more thoughtful and slower relationship development, potentially delaying decisions about marriage and having children.
- Economic and Career Considerations: The movement has also highlighted gender inequalities in the workplace, prompting many women to focus on their careers and financial independence before considering starting a family.
- Psychological Impact: For some, the movement has brought up past traumas and led to a reevaluation of personal priorities and relationships. This can influence decisions about marriage and parenthood.
Influence of Wokeism:
“Wokeism,” can influence birth rates in several ways. These include:
- Changing Social Norms: The emphasis on social justice and equality can lead to shifts in traditional family structures and roles. People may prioritize personal development, career goals, and social activism over starting a family.
- Economic and Career Focus: With a strong focus on addressing systemic inequalities, many individuals may choose to invest more time in their careers and financial stability before considering marriage and children.
- Gender Equality: The push for gender equality can lead to more balanced domestic responsibilities and career opportunities for women. This can result in delayed family planning as both partners may focus on their careers.
- Environmental Concerns: Wokeism often includes a strong environmental component, with concerns about overpopulation and sustainability. Some people may choose to have fewer children or none at all to reduce their environmental footprint.
- Support for Diverse Family Structures: There is greater acceptance of diverse family structures, including single parenthood, cohabitation without marriage, and same-sex parenting. This can lead to different timelines and approaches to family planning.
BirthStrike Like Movements:
BirthStrike is a movement founded by Blythe Pepino in 2019, primarily in the UK, to raise awareness about the severe threats posed by climate change and how these threats influence decisions about having children. BirthStrike members, who are mostly young women, publicly declare their decision not to have children due to fears about the future impacts of climate change. BirthStrike helped to humanize the climate crisis by connecting it to deeply personal decisions about family planning. BirthStrike has played a significant role in bringing attention to the existential threats of climate change and how they affect personal decisions about having children. It underscores the deep connections between environmental activism and individual life choices. Some of the impact are:
- Psychological and Social Impact: BirthStrike provided a platform to express their anxieties about the future and find solidarity with others who share similar concerns and also starting the family. This collective action also served as a form of protest, aiming to pressure governments and corporations to take more decisive action on climate change.
- Broader Influence: BirthStrike is part of a larger trend where environmental concerns influence reproductive decisions. Similar movements, like Conceivable Future in the U.S. and No Future No Children in Canada, also highlight the intersection of climate anxiety and family planning.
Technoference:
The interference of technology in personal relationships, can have several indirect impacts on birth rates:
- Relationship Quality: Technoference can lead to decreased relationship satisfaction and increased conflict. When partners feel neglected due to excessive technology use, it can strain the relationship, potentially leading to lower levels of intimacy and connection. This strain can reduce the likelihood of couples deciding to have children.
- Reduced Communication: Constant interruptions from technology can hinder meaningful communication between partners. Effective communication is crucial for resolving conflicts and making joint decisions, including those about starting a family.
- Increased Stress and Anxiety: The constant presence of technology can contribute to higher stress and anxiety levels. This can affect mental health and overall well-being, making individuals less inclined to consider having children.
- Work-Life Balance: Technology often blurs the boundaries between work and personal life. The pressure to be constantly available for work can reduce the time and energy couples have for each other, impacting their decisions about family planning.
- Parent-Child Relationships: For existing parents, technoference can affect the quality of interactions with their children. Parents distracted by technology may be less responsive and engaged, which can impact their desire to expand their family.
The Divorce Pandemic:
The trend of increasing divorce rates, often referred to as the “divorce pandemic,” has been influenced by several factors:
- Economic Stress: Financial instability, exacerbated by the COVID-19 pandemic, has put a strain on many marriages. Job losses, reduced income, and economic uncertainty can lead to increased marital conflict and, ultimately, divorce.
- Changing Social Norms: There is less stigma associated with divorce today compared to previous generations. This shift in societal attitudes makes it easier for individuals to consider divorce as an option when facing marital difficulties.
- Later-Life Divorces: Known as “gray divorces,” the rate of divorce among adults aged 50 and older has surged. This trend is partly due to the baby boomer generation, who are more likely to seek divorce later in life compared to previous generations. This is impacting younger generations to evaluate marriage as an option.
- Pandemic-Related Stress: The COVID-19 pandemic has intensified existing marital issues for many couples. Lockdowns, quarantine measures, and the stress of managing work and family life from home have contributed to a rise in divorce rates.
- Personal Growth and Independence: There is a growing emphasis on personal growth and independence. Many individuals, especially women, are more financially independent and feel empowered to leave unsatisfactory marriages.
The Dating Apps Raps:
Digital dating apps have significantly transformed the landscape of romantic relationships. but they also come with several negative impacts, including people finding the right choice for the younger generations and delay in finding a life-long relationship to settle down and start a family. These include:
- Mental Health Issues: Frequent use of dating apps can lead to mental health problems such as anxiety, depression, and low self-esteem. The constant exposure to rejection and the pressure to present an idealized version of oneself can be damaging.
- Superficial Judgments: Dating apps often encourage users to make quick judgments based on appearance. This can lead to superficial connections and a focus on physical attributes over deeper compatibility.
- Addictive Behavior: The design of many dating apps, with their swipe-based interfaces, can be addictive. Users may spend excessive amounts of time on these apps, which can interfere with their daily lives and relationships.
- Ghosting and Rejection: The ease of ending communication without explanation, known as ghosting, is common on dating apps. This behavior can be emotionally hurtful and lead to feelings of insecurity and mistrust in the process.
- Harassment and Safety Concerns: Many users, particularly women, report experiencing harassment, unsolicited explicit messages, and other forms of inappropriate behavior on dating apps. This can create a hostile and unsafe environment and mistrusts for the future relationship.
- Decreased Relationship Satisfaction: Some studies suggest that relationships formed through dating apps may have lower levels of satisfaction and stability compared to those formed through traditional means. The abundance of choices can lead to a “grass is greener” mentality, where users are always looking for a better match.
There are around 20 countries which are experiencing negative population growth. Moreover, more than 100 countries and territories have fertility rates below the replacement level of 2.1 births per woman. While India is still not at that cusp of replacement level of 2.1 births. But it is certain that a Ministry of Sex measures are required for more than 50 countries given their demographics. However, some of the countertrends could accelerate this even faster.